<< Go Back to PicketBox Overview
PicketBox (Formerly JBoss Security) provides audit capabilities for Java Applications.
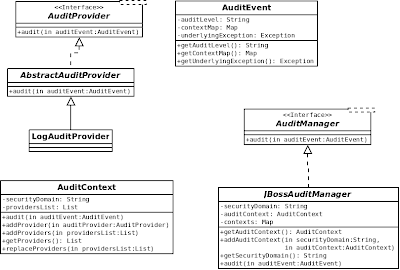
Audit Providers
The Audit Providers form the cornerstone of the PicketBox audit framework. By default, a LogAuditProvider is provided as part of the framework.
Audit Event
The AuditEvent is an object that is the carrier of the audit information. An AuditEvent gets logged by the Audit Provider.
Audit Manager
AuditManager is the entry into the auditing framework that is available as part of the security domain under which the authentication/authorization features were utilized.
Class Diagram
Sample Code
In this example, we are going to use PicketBox for authentication. After that, we use the auditing feature to audit the authentication event.
//Imports
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.security.auth.Subject;
import org.jboss.security.AuthenticationManager;
import org.jboss.security.audit.AuditEvent;
import org.jboss.security.audit.AuditLevel;
import org.jboss.security.audit.AuditManager;
import org.jboss.security.audit.AuditProvider;
import org.picketbox.config.PicketBoxConfiguration;
import org.picketbox.factories.SecurityFactory;
//A private variable
private final String securityDomainName = "test";
//Test method to test authentication and then audit
public void testValidAuthentication() throws Exception
{
SecurityFactory.prepare();
try
{
String configFile = "config/audit.conf";
PicketBoxConfiguration idtrustConfig = new PicketBoxConfiguration();
idtrustConfig.load(configFile);
AuthenticationManager am = SecurityFactory.getAuthenticationManager(securityDomainName);
assertNotNull(am);
Subject subject = new Subject();
Principal principal = getPrincipal("anil");
Object credential = new String("pass");
boolean result = am.isValid(principal, credential, subject);
assertTrue("Valid Auth", result);
assertTrue("Subject has principals", subject.getPrincipals().size() > 0);
Map<String,Object> contextMap = new HashMap<String,Object>();
AuditEvent auditEvent = new AuditEvent(AuditLevel.SUCCESS,contextMap);
AuditManager auditManager = SecurityFactory.getAuditManager(securityDomainName);
auditManager.audit(auditEvent);
assertTrue("Audit Event is contained in the static map of Audit Provider",
TestAuditProvider.eventList.contains(auditEvent));
}
finally
{
SecurityFactory.release();
}
}
private Principal getPrincipal(final String name)
{
return new Principal()
{
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
};
}
public static class TestAuditProvider implements AuditProvider
{
public static List<AuditEvent> eventList = new ArrayList<AuditEvent>();
public void audit(AuditEvent auditEvent)
{
eventList.add(auditEvent);
}
}
The configuration file "audit.conf" looks as follows:
<?xml version='1.0'?> <policy xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="urn:jboss:security-config:5.0" xmlns="urn:jboss:security-config:5.0" xmlns:jbxb="urn:jboss:security-config:5.0"> <application-policy name = "test"> <authentication> <login-module code = "org.jboss.security.auth.spi.UsersRolesLoginModule" flag = "required"> </login-module> </authentication> <audit> <provider-module code="org.picketbox.test.api.AuditUnitTestCase$TestAuditProvider"/> </audit> </application-policy> </policy>
In this example, we used a TestAuditProvider that has a list to store the audit events. In your applications, you should either write your own AuditProvider or reuse the LogAuditProvider.
org.jboss.security.audit.providers.LogAuditProvider
Note: The LogAuditProvider utilizes the JBoss Logging SPI. Because of this, it is possible to log the audit events either in log4j or JDK logs.
PicketBox Audit using Java Annotation
You can use the @Audit annotation on Java classes. Please refer to PicketBox Authorization article. The annotation is described in PicketBoxSecurityAnnotations.
References
Comments