Hi
This Article i describe how to create Datasource in JBoss AS 7.
If you are using the 1.6 JVM, then you should Download JDBC4 postgresql Driver.
Install the JDBC4 postgresql Driver as a JBoss 7 deployment
- After downloading postgressql driver jar file. just move the postgressql driver jar file into Jboss 7 installation directory under standalone/deployments (jboss-as-web-7.0.0.Final/standalone/deployments).
- Restart your jboss server
- Then go to the url and type http://localhost:8080/
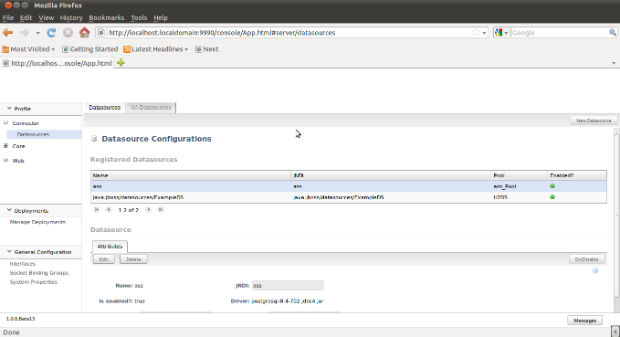
- click Administration console.
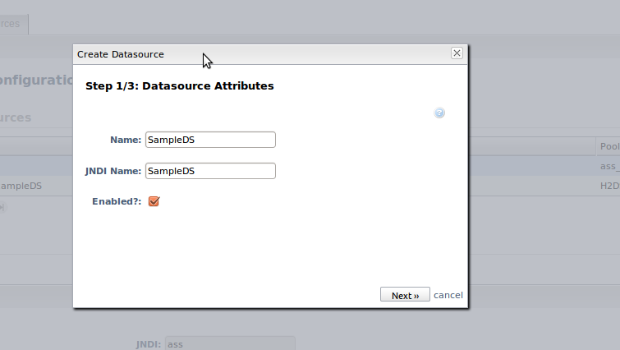
In Jboss Administration console you can press New datasource button, enter datasource name and jndi name then click next button.
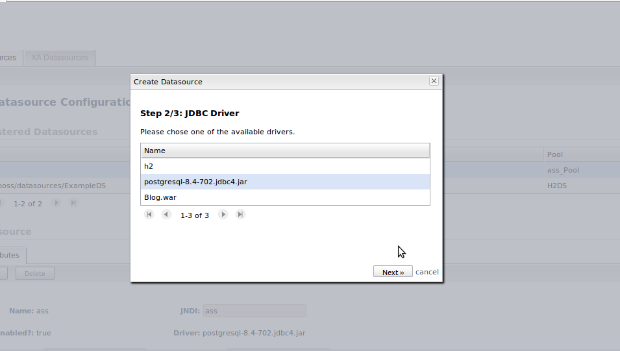
step 2 : select postgresql driver. click Next
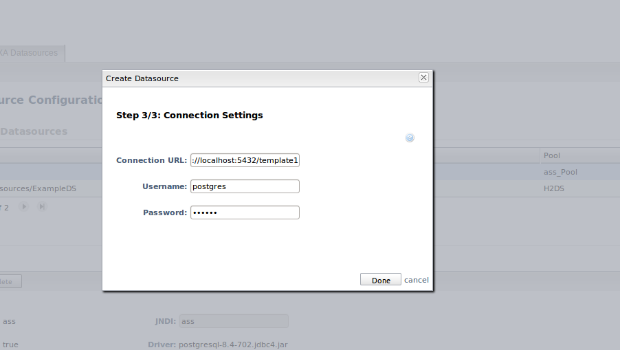
Step 3: enter connection URL jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/template1 , Username and Password.
finally click Done.
Testing the Postgressql Datasource
Using the test client you may now verify the proper installation of your datasource.
<%@page
import="java.util.*,javax.naming.*,javax.sql.DataSource,java.sql.*"%>
<%
DataSource ds = null;
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
InitialContext ic;
try {
ic = new InitialContext();
ds = (DataSource) ic.lookup("java:/SampleDS");
con = ds.getConnection();
stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from login");
while (rs.next()) {
out.println("<br> " + rs.getString("username") + " | "
+ rs.getString("password"));
}
rs.close();
stmt.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
out.println("Exception thrown ");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
}
%>
Comments